Overview of Cell Proliferation
Cell proliferation is an increase in cell number due to cell division, or cytokinesis, the final step of the cell cycle. Cell proliferation is necessary for normal tissue development and maintenance over the lifespan.
Cell proliferation is a tightly regulated process, with many different proteins controlling cell cycle checkpoints. Genetic mutations found in cancer cells cause uncontrolled cellular proliferation.
How to Measure Cell Proliferation
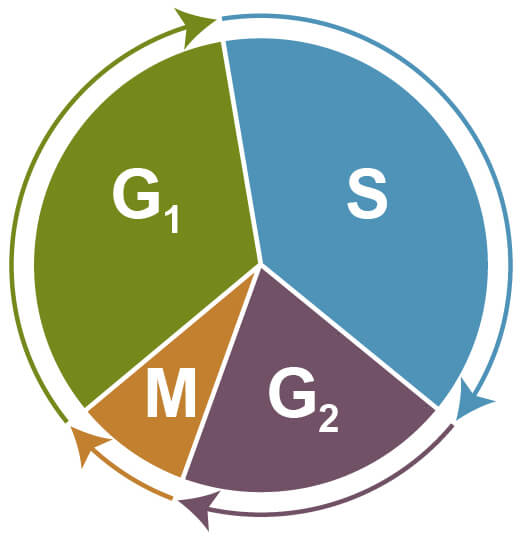
The cell cycle is composed of multiple phases, including the G1 phase where cells increase in size, the S phase where DNA is newly synthesized, the G2 phase where further cell growth occurs, and finally the M, or mitosis, phase where the cell ultimately divides. Some cells exit the cell cycle and stop dividing altogether; this is known as quiescence or resting state (G0)
Phases of the Cell Cycle: G1 - increasing size; S - DNA synthesis and replication; G2 - growth; M - mitosis and cell division; G0 - quiescent.
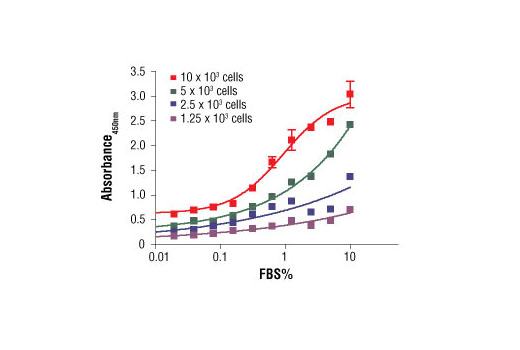
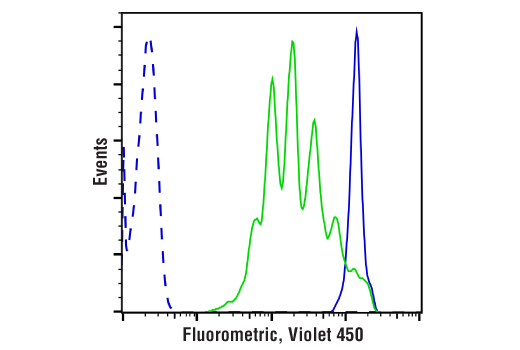
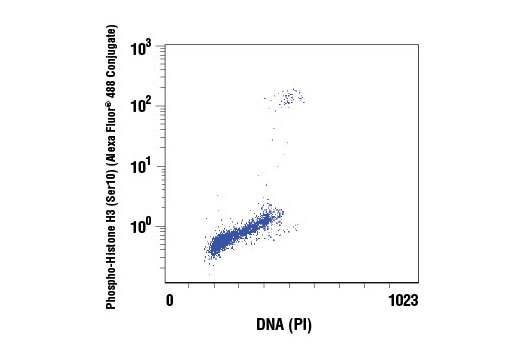
Two of the most common ways of measuring cell proliferation include cell cycle assays and proliferation assays, which rely on the incorporation of propidium propidium iodide or BrdU into DNA:
Assay
BrdU Cell Proliferation Assay Kit
What is Measured
Measures the level of DNA synthesis occuring during cellular proliferation.
Assay
What is Measured
Measures cell division using amine-reactive dyes and the principle of dye dilution to trace multiple rounds of cell proliferation, via flow cytometry.
Assay
What is Measured
Quantifies the number of cells at different stages of the cell cycle based on the profile of their DNA.
Markers to Determine Cell Proliferation
Another common method for measuring cell proliferation is by examining the expression levels of cell cycle proteins and other proteins required for proliferation. Some common protein markers for proliferating cells include:
Proliferation Marker
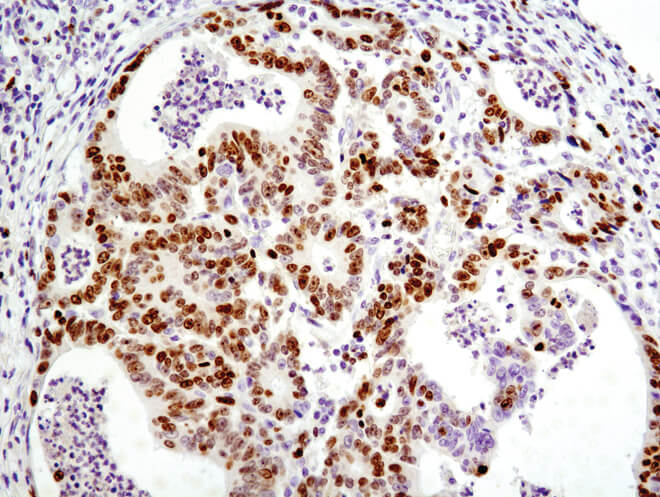
Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PNCA)
Proliferation Marker Description
DNA sliding clamp protein that plays an important role in DNA replication.
Proliferation Marker
Proliferation Marker Description
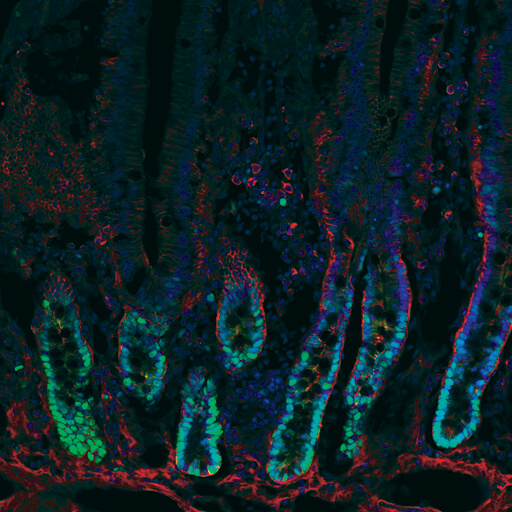
Non-nuclear histone protein only expressed at high levels in proliferating cells.
Proliferation Marker
Proliferation Marker Description
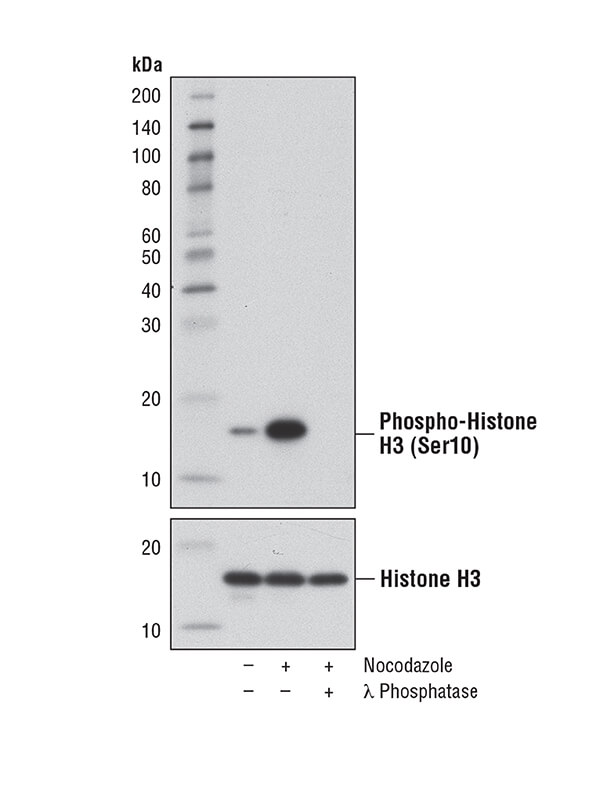
Nuclear histone protein that is phosphorylated in proliferating cells.
Proliferation Marker
Proliferation Marker Description
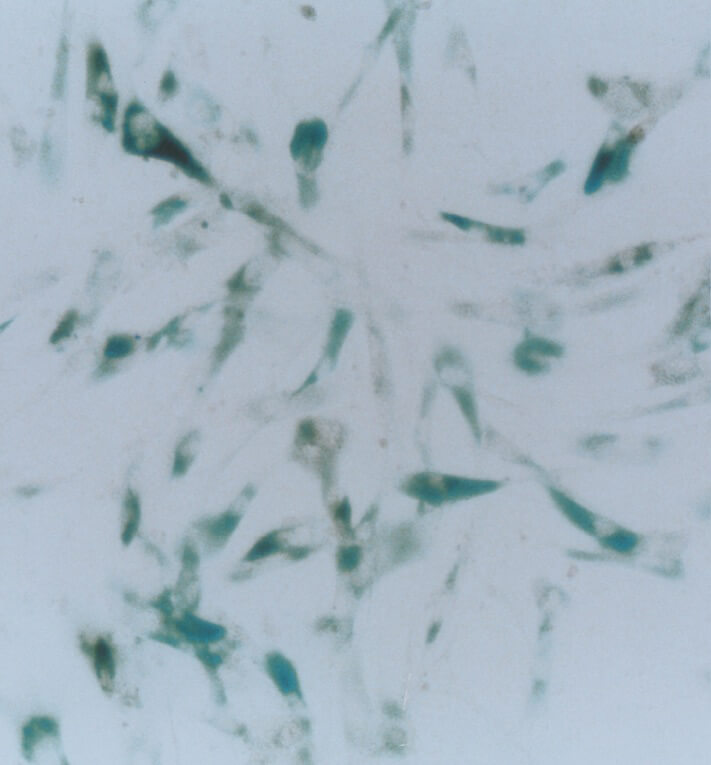
β-galactosidase activity is associated with senescent cells that are not proliferating.